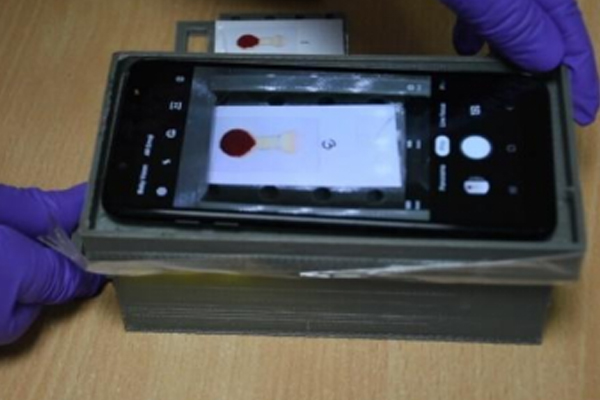
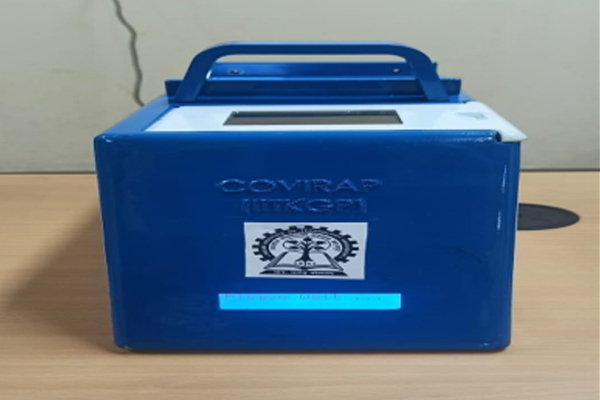
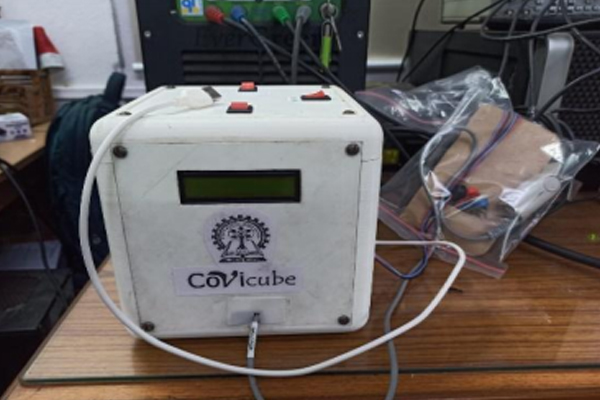
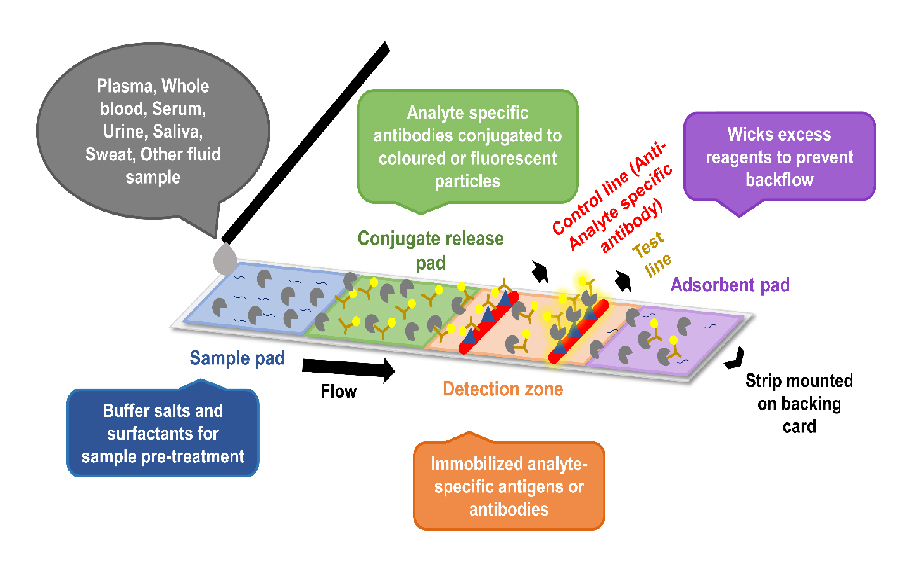
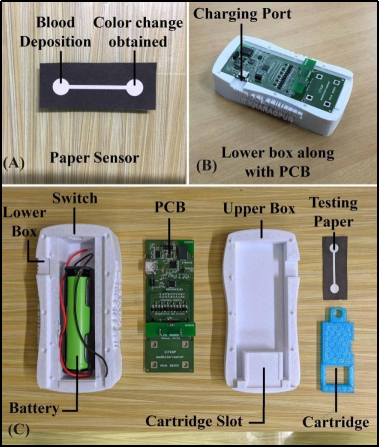
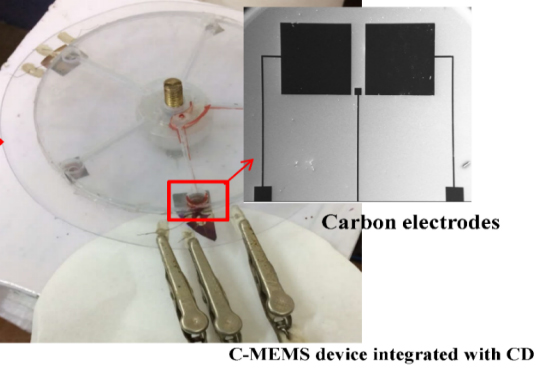
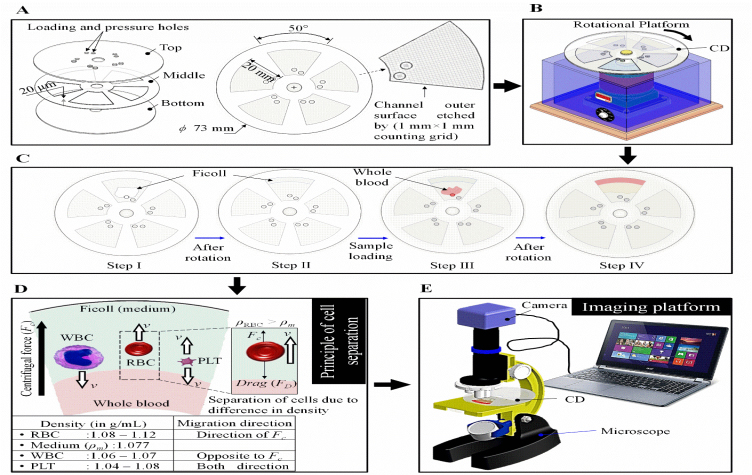
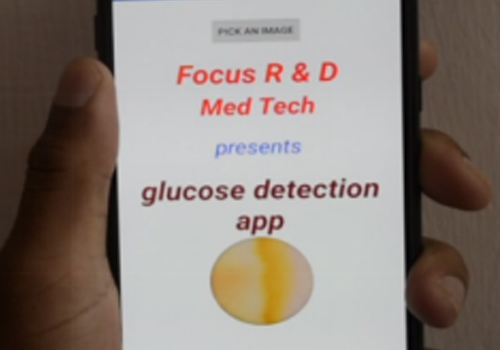
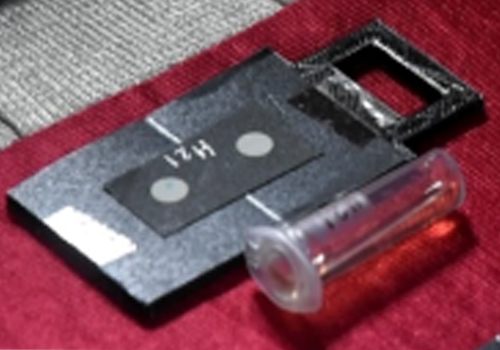
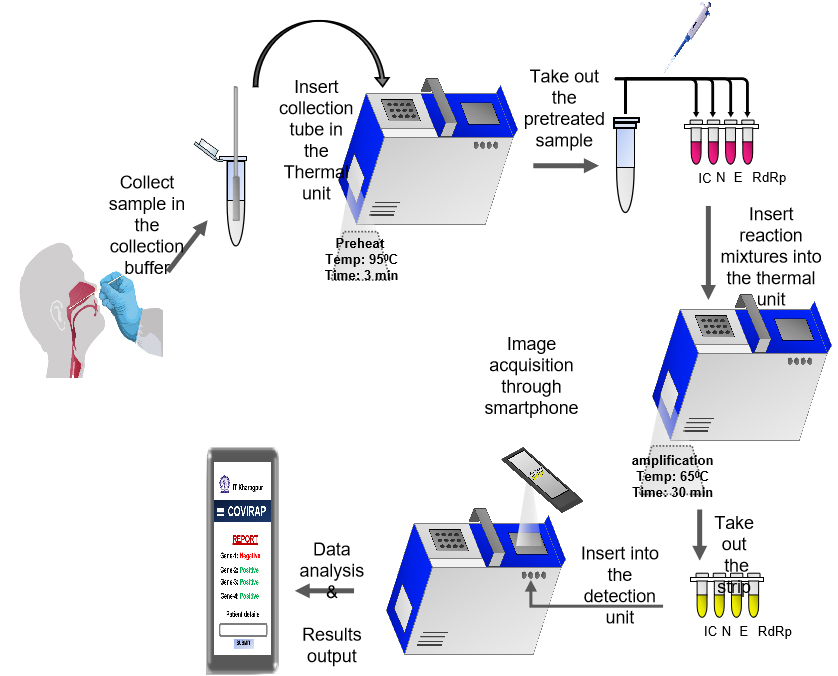
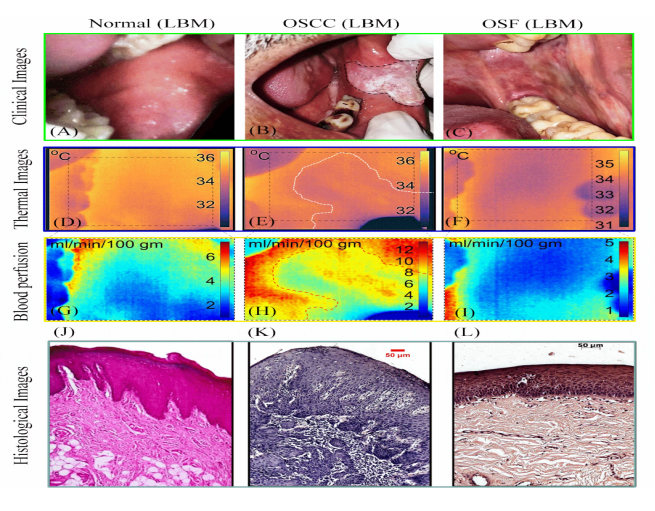
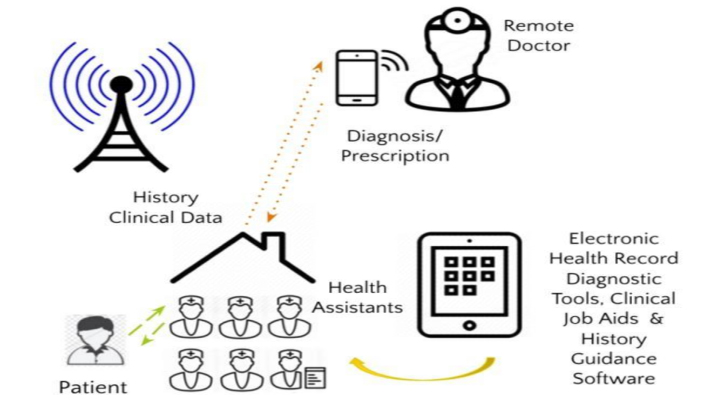
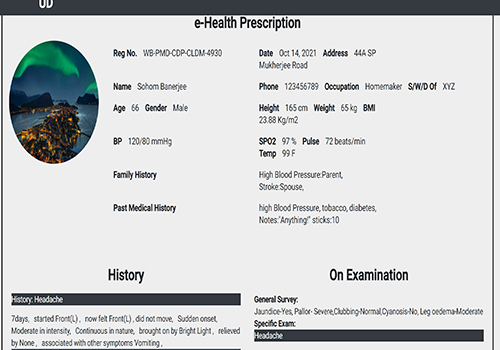
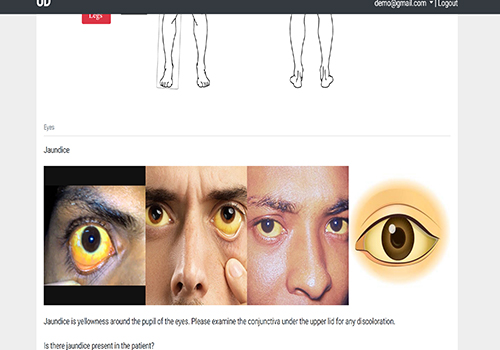
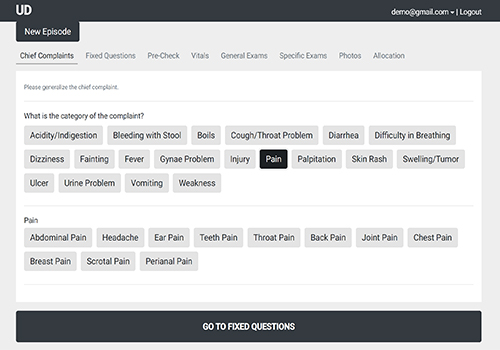
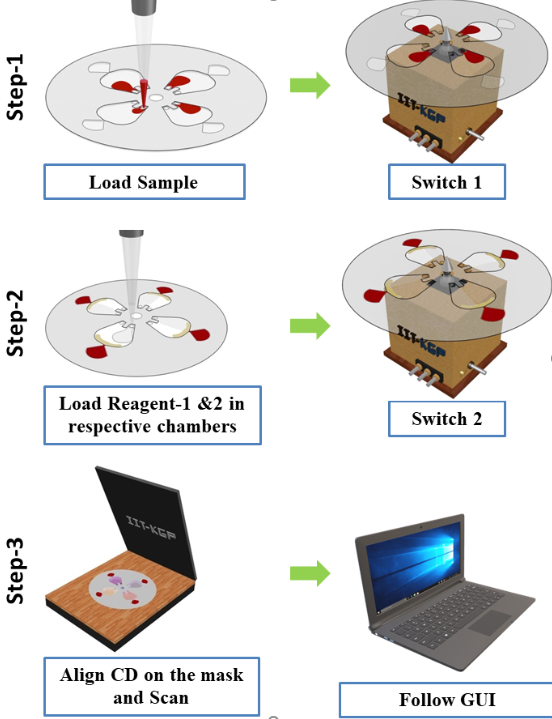
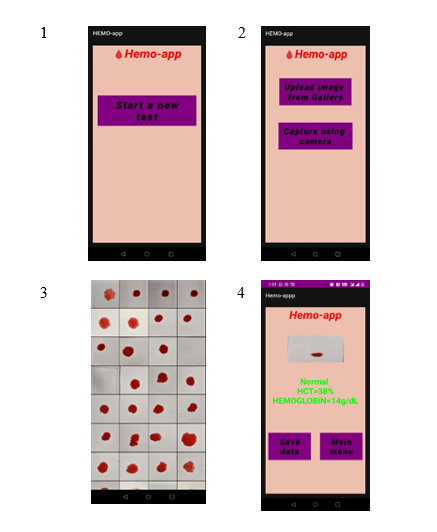
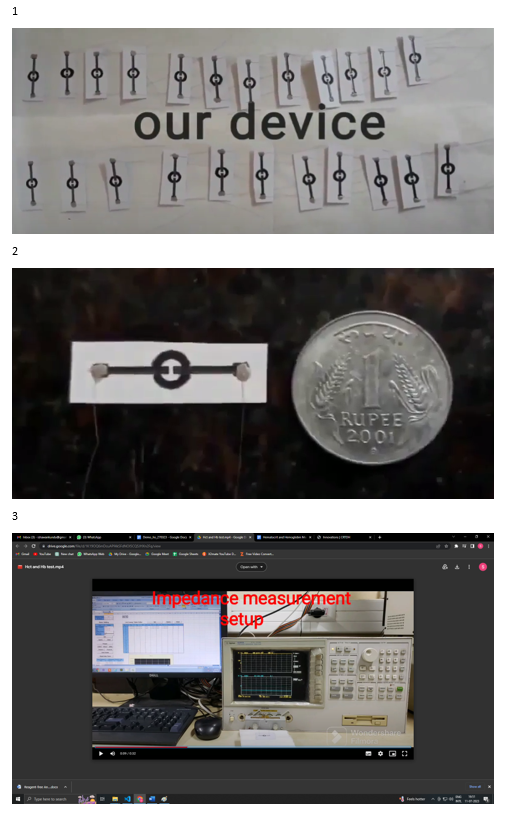
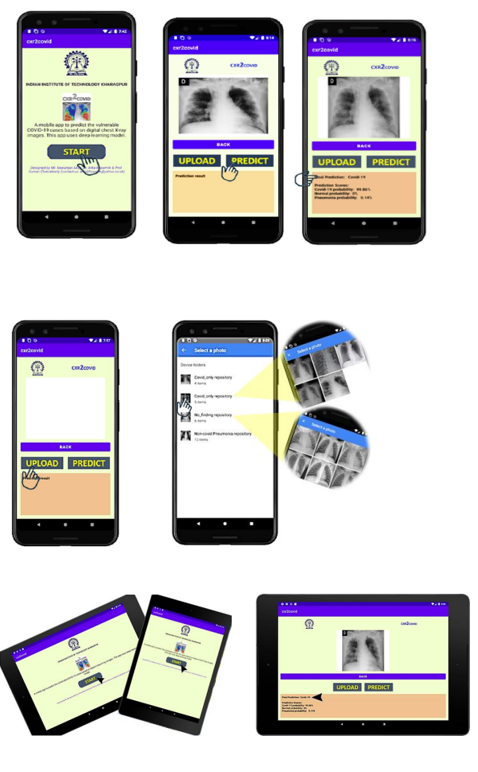
Diagnostics with 1-Drop of Body Fluid at the Point of Care
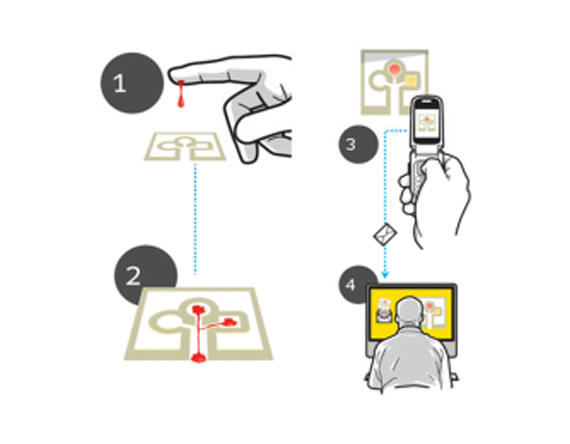
Advantages
Portable and thus spot diagnosis is possible
Functional with limited resources
Easy handling
Mass fabrication is possible
Inexpensive
Involvement of minimal infrastructures
Rapid and easy monitoring
Automated